
If you have ever noticed extra details in Google search results, such as star ratings, event times, or recipe images, you have already seen schema markup in action. Schema markup is a type of code that helps search engines understand your website content better. It acts like a translator between your site and search engines, giving them more context about what each page means.
Adding schema markup is important for SEO because it improves how your website appears in search results. Instead of just showing a plain link, schema can highlight reviews, FAQs, products, and much more. This makes your listing stand out from others and attracts more clicks.
The benefits are clear. Schema markup can increase your click-through rate, boost your visibility in search results, and make your website look more professional. When people ask what schema markup is in SEO, the answer is simple: it is a powerful tool that makes your site easier for search engines to understand and more appealing to potential visitors.
Schema markup in SEO is a form of structured data that you add to your website to give search engines extra information about your content. In simple terms, it tells search engines exactly what your page is about. For example, if you publish a recipe, the schema can let Google know the cooking time, ingredients, and even calories.
Search engines use this information to create enhanced search results called rich snippets. These snippets can display images, reviews, prices, or other details directly on the results page, making your link more attractive to users.
It is important to understand the difference between structured data, schema.org, and schema markup. Structured data is the general method of organizing information for search engines. Schema.org is the official library where all schema types and formats are listed. Schema markup is the actual code you place on your site using those definitions.
When people ask what is schema markup SEO, the answer is that it is an essential technique for improving visibility, helping your site stand out, and guiding search engines to display your content in the best way possible.
Understand how semantic SEO focuses on search intent, context, and meaning, and why it matters for modern optimization.
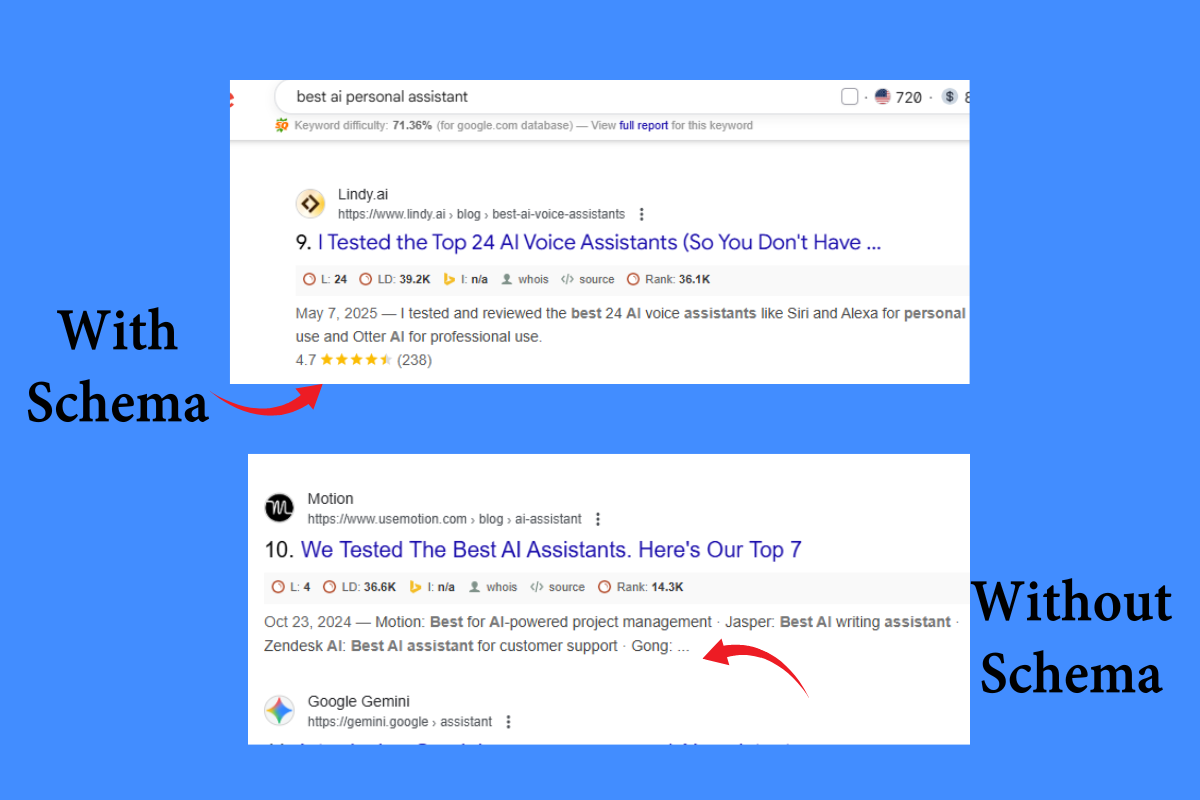
Schema markup matters because it directly improves the way your website appears in search results. When you use schema, Google can display rich snippets such as star ratings, product prices, event dates, and review summaries. These extra details make your listing stand out and help users quickly find what they are looking for.
One of the biggest advantages of schema markup is the increase in click-through rate (CTR). A plain blue link in search results can easily get lost among competitors, but a result with reviews, images, or FAQs attracts more attention. More clicks mean more visitors to your website, which is a key goal of SEO.
Schema is also valuable for local businesses. Local business schema helps search engines display your business name, location, phone number, and even customer reviews. This can improve your visibility in Google’s local search results and Google Maps, making it easier for customers to find you.
Real-world examples are easy to spot. If you search for a recipe, you will often see results with images, star ratings, and cooking times. Product searches may show prices and stock availability. Event searches can display dates and ticket information. All of these enhancements are powered by schema markup.
According to Google’s Search Central and Schema.org, structured data is recommended for websites that want to improve how content is presented in search results. Using schema markup not only helps search engines understand your content but also makes your website more appealing to users.
There are several schema types that websites can use depending on their content. Here are some of the most common ones:
Choosing the right schema makes your content easier for search engines to interpret and more useful for users browsing search results.
When adding schema markup to a website, there are three main formats supported by Google. These are JSON-LD, Microdata, and RDFa. Each has its own advantages and use cases, but most websites today prefer one over the others.
If you are wondering what the recommended format for implementing schema markup is, the answer is JSON-LD. It is simple, clean, and directly supported by Google. This makes it the best choice for most websites.
Adding schema markup may sound technical, but it can be done in a few simple steps. You can either add the code manually or use tools that generate a schema for you. Here’s a beginner-friendly guide:
Schema markup helps search engines better understand your content and improves your chances of appearing with rich snippets. Even small updates, such as adding FAQ schema, can make a big difference in how users interact with your site in search results.
If you are running a WordPress website, adding schema markup is easier than you might think. You can either use plugins or add the code manually, depending on your comfort level.
Using a plugin is ideal for beginners because it requires no coding knowledge. You simply install the plugin, choose the schema type, and fill in the details.
If you use page builders like Elementor or Divi, or Gutenberg, many have built-in schema features or integrations with SEO plugins. This gives you more flexibility when designing structured content.
Tip: Always test your schema after adding it to make sure Google can read it correctly. If you want a hassle-free method, plugins like Rank Math or Schema Pro are the easiest choice.
Adding schema markup in WordPress can boost your search visibility and make your site more engaging in search results without needing advanced technical skills.
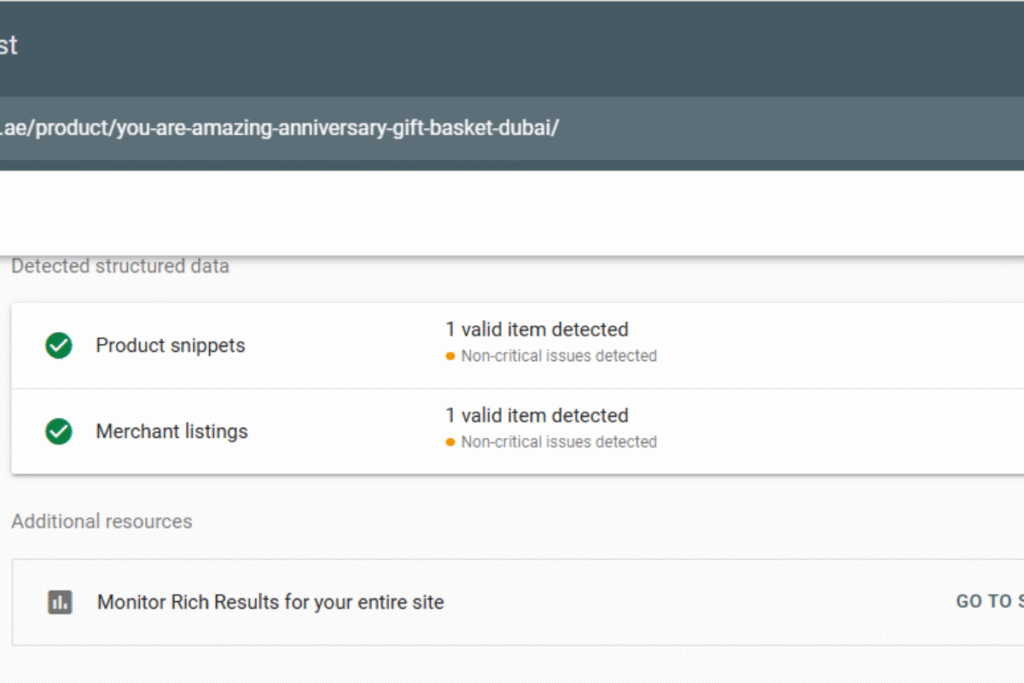
While schema markup can improve your SEO, using it incorrectly may lead to errors or even penalties from Google. Here are some common mistakes to watch out for:
Avoiding these mistakes ensures your schema markup works as intended. Proper testing and validation help your website qualify for rich snippets and maintain trust with search engines.
Adding schema markup is only effective when it is done correctly. Following best practices ensures that your website benefits from rich results and avoids errors. Here are some key tips:
By following these best practices, you ensure that your schema markup improves your SEO, enhances your visibility in search results, and builds trust with both search engines and users.
Schema markup is one of the most effective ways to help search engines understand your website and display it in an attractive way in search results. By using schema, you can unlock rich snippets such as ratings, product details, FAQs, and event information that make your listings stand out.
Throughout this guide, we have explained what schema markup is, why it matters for SEO, and the different types you can use. We also covered the recommended format, step-by-step instructions for adding schema, WordPress options, common mistakes, and best practices.
The answer to “what is schema markup in SEO” is simple. It is a tool that connects your content with search engines in a structured way, giving your website a better chance of appearing at the top with enhanced results.
If you have not yet implemented schema markup, now is the time to start. Even small steps like adding an FAQ or a Product schema can make a big difference in click-through rates and visibility. Test your code, follow Google’s guidelines, and keep your schema updated.
Schema markup is not complicated once you know the basics, and it can quickly become a powerful asset in your SEO strategy.
Schema markup is a type of structured data code that helps search engines understand your website content. It improves how your pages appear in search results by enabling rich snippets like ratings, prices, and FAQs.
Google recommends using JSON-LD format because it is simple to add, easy to maintain, and does not interfere with your website design.
You can add schema manually by placing JSON-LD code in your site’s header, or you can use tools such as Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper and plugins like Rank Math or Yoast SEO for WordPress.
Yes. Plugins like Rank Math, Schema Pro, or Yoast SEO make it easy to add schema types such as Product, FAQ, or Local Business without writing any code.
Schema markup itself does not directly increase rankings, but it improves how your website appears in search results. Rich snippets attract more clicks, which can indirectly boost your SEO performance.


Welcome to Scope Signal, your trusted destination for clear, practical, and research-driven technology content.
At Scope Signal, we don’t just write about tech — we break it down, analyze it, and explain it in a way that actually makes sense. Whether you’re a beginner trying to understand a new tool or a professional looking for in-depth insights, our goal is to make technology simple, useful, and actionable.